Infrared radiation, often simply referred to as infrared or IR, is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths longer than those of visible light, but shorter than microwaves. This type of radiation is invisible to the human eye, yet it plays a crucial role in various natural and technological processes. Infrared radiation is commonly associated with heat, as it is emitted by any object with a temperature above absolute zero. The Earth, for example, radiates infrared heat into space.
In technology, infrared radiation is extensively used in applications such as infrared spectroscopy, night vision devices, and communication systems.
Additionally, it has widespread applications in medical imaging, where infrared radiation is harnessed for thermal imaging to detect variations in temperature. The unique properties of infrared radiation make it a valuable tool in scientific research, industrial processes, and everyday technologies that enhance our understanding of the world and improve our quality of life.
Benifit of Infra red radiation
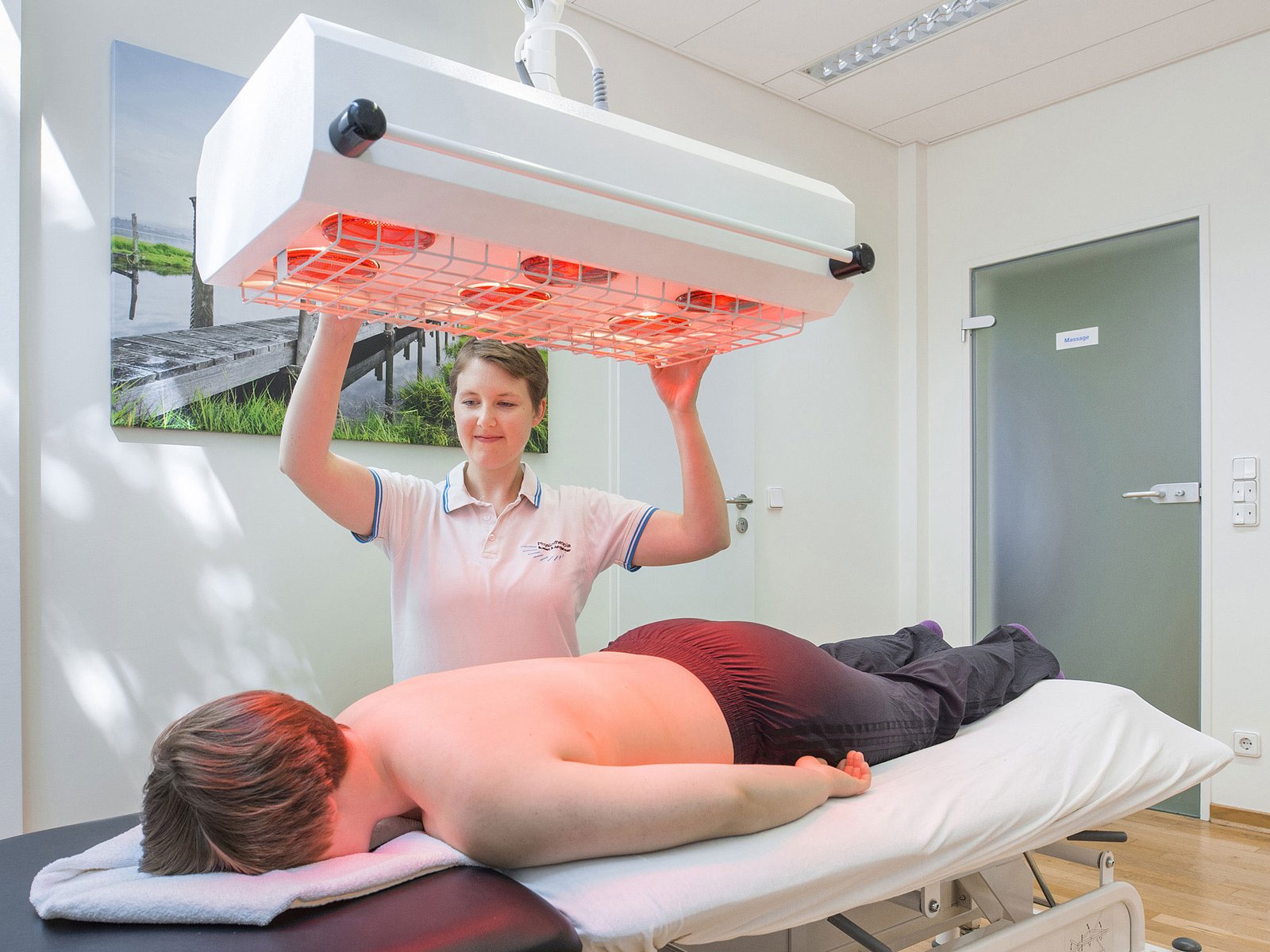
 The benefits of infrared radiation are diverse and span various fields, ranging from healthcare to industrial applications. One of the primary advantages lies in its use for thermal imaging, enabling the visualization of temperature variations in objects and living organisms. In the medical field, infrared radiation is employed in thermography to detect abnormalities or changes in body temperature, aiding in the early diagnosis of conditions such as inflammation or circulatory disorders. Infrared heaters, commonly used for therapeutic purposes, emit infrared radiation to efficiently and directly heat objects and bodies without significantly heating the surrounding air. This targeted heating is not only energy-efficient but also provides relief for conditions like muscle pain and arthritis.
The benefits of infrared radiation are diverse and span various fields, ranging from healthcare to industrial applications. One of the primary advantages lies in its use for thermal imaging, enabling the visualization of temperature variations in objects and living organisms. In the medical field, infrared radiation is employed in thermography to detect abnormalities or changes in body temperature, aiding in the early diagnosis of conditions such as inflammation or circulatory disorders. Infrared heaters, commonly used for therapeutic purposes, emit infrared radiation to efficiently and directly heat objects and bodies without significantly heating the surrounding air. This targeted heating is not only energy-efficient but also provides relief for conditions like muscle pain and arthritis.
In industrial settings, infrared radiation plays a key role in processes such as materials testing, welding, and drying, where precise temperature control is essential. Furthermore, infrared communication technology, found in remote controls and wireless devices, enables data transmission without the need for physical connections. The versatile applications of infrared radiation underscore its significance in enhancing medical diagnostics, facilitating industrial processes, and contributing to the convenience and efficiency of everyday technologies.
Infra red radiation F&Q's
Infrared radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths longer than those of visible light but shorter than microwaves. It is commonly associated with heat and is emitted by objects with temperatures above absolute zero.
Infrared radiation is used in thermal imaging to visualize temperature variations in objects and living organisms. This technology is applied in fields such as medicine for early detection of conditions like inflammation or circulatory disorders.
Infrared radiation is employed in medical applications, particularly in thermography, for detecting changes in body temperature. It aids in early diagnosis by identifying abnormalities and variations in temperature related to specific health conditions.
In therapeutic settings, infrared radiation is harnessed in heaters to provide targeted and efficient heating of objects and bodies. This method is utilized for pain relief, especially in conditions such as muscle pain and arthritis.
In industrial settings, infrared radiation is crucial for processes like materials testing, welding, and drying. Its precise temperature control capabilities make it valuable in ensuring the efficiency and quality of various manufacturing processes.
Infrared communication technology enables wireless data transmission and is commonly found in devices like remote controls. It utilizes infrared radiation to transmit signals between devices without the need for physical connections, offering convenience in everyday technologies.
